
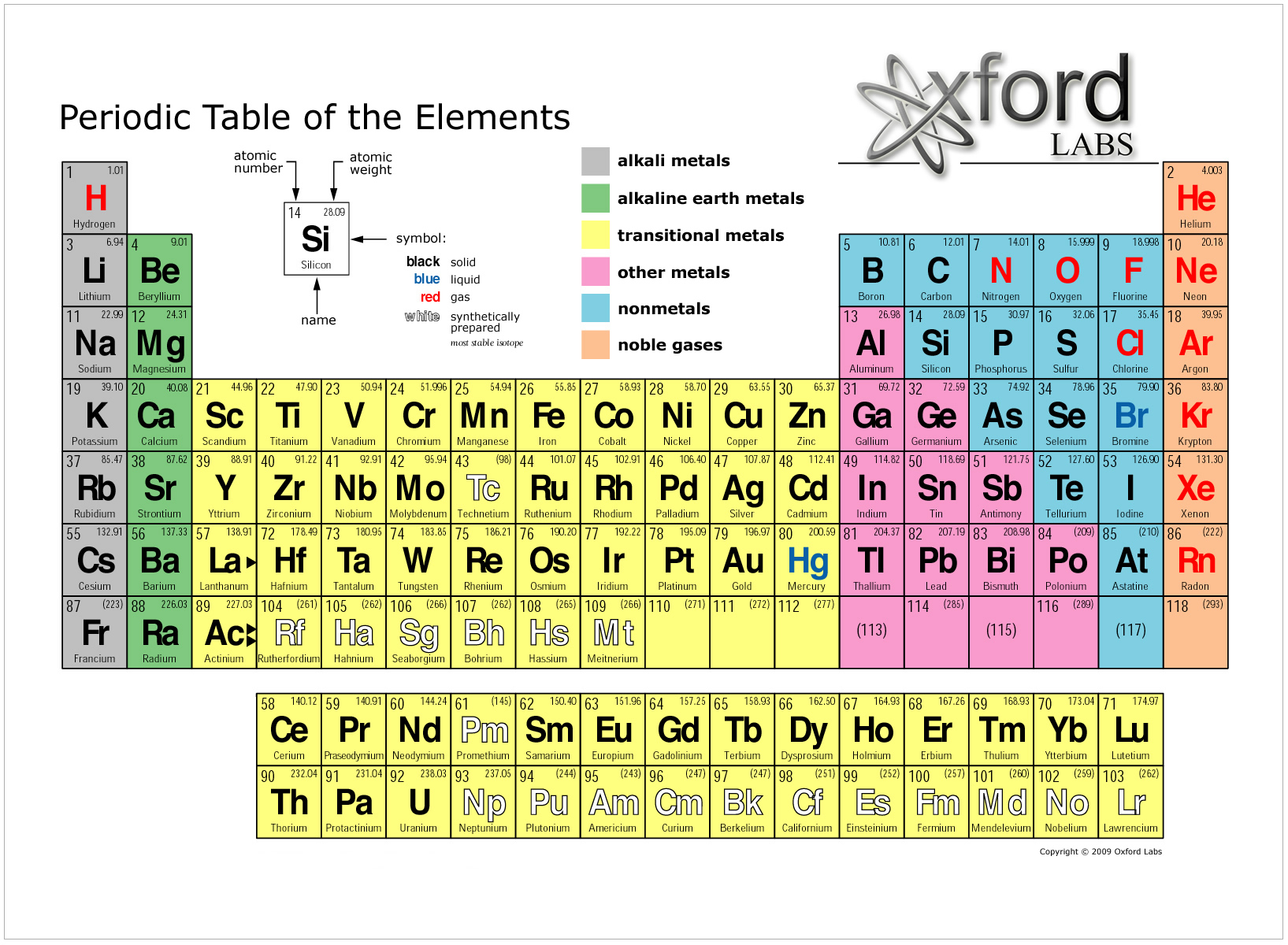
Ītoms can be subdivided into different types based on the number of protons (and thus also electrons) they have. When atoms participate in chemical reactions, they may gain or lose electrons to form positively- or negatively-charged ions or they may share electrons with each other instead. Electrons participate in chemical reactions, but the nucleus does not. Atoms consist of a small positively charged nucleus, made of positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons the charges cancel out, so atoms are neutral. Atoms are extremely small, being about one ten-billionth of a meter across thus their internal structure is governed by quantum mechanics. The smallest constituents of all normal matter are known as atoms. Many alternative representations of the periodic law exist, and there is some discussion as to whether there is an optimal form of the periodic table.ģD views of some hydrogen-like atomic orbitals showing probability density and phase (g orbitals and higher are not shown) Some scientific discussion also continues regarding whether some elements are correctly positioned in today's table. It is not yet known how far the table will stretch beyond these seven rows and whether the patterns of the known part of the table will continue into this unknown region. Today, all the first 118 elements are known, completing the first seven rows of the table, but chemical characterisation is still needed for the heaviest elements to confirm that their properties match their positions. In nature, only elements up to atomic number 94 exist to go further, it was necessary to synthesise new elements in the laboratory.

The periodic table continues to evolve with the progress of science. The periodic table and law are now a central and indispensable part of modern chemistry. Seaborg's 1945 discovery that the actinides were in fact f-block rather than d-block elements, a recognisably modern form of the table was reached. The periodic law was recognized as a fundamental discovery in the late 19th century, and it was explained with the discovery of the atomic number and pioneering work in quantum mechanics of the early 20th century that illuminated the internal structure of the atom. Because not all elements were then known, there were gaps in his periodic table, and Mendeleev successfully used the periodic law to predict properties of some of the missing elements. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869: he formulated the periodic law as a dependence of chemical properties on atomic mass. The underlying reason for these trends is electron configurations of atoms. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character (keeping their own electrons) increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character (surrendering electrons to other atoms) increasing in the opposite direction. Elements from the same column group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit a periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the ( chemical) elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
